Introduction
In an environment where modern applications demand maximum performance, high availability and low latency, speed, scalability and reliability are essential requirements in any database system. Organizations need database solutions that not only meet their needs today, but are also future-proof.
In this context, AlloyDB emerges as a strategic proposal of Google Cloud in the field of relational databases for the enterprise environment, which combines the robustness and flexibility of the open source ecosystem of PostgreSQL, with the power and reliability of an enterprise-level cloud infrastructure such as Google Cloud Platform (GCP), offering a modern, scalable and ready to face critical workloads platform.
AlloyDB is positioned as an ideal solution for:
- Companies looking to modernize Oracle or SQL Server, environments, avoiding proprietary licenses.
- Critical workloads requiring high availability, low maintenance and dynamic scalability.
- Teams already working on Google Cloud and need to easily integrate artificial intelligence capabilities, advanced analytics and serverless services.
Introduction
In an environment where modern applications demand maximum performance, high availability and low latency, speed, scalability and reliability are essential requirements in any database system. Organizations need database solutions that not only meet their needs today, but are also future-proof.
In this context, AlloyDB emerges as a strategic proposal of Google Cloud in the field of relational databases for the enterprise environment, which combines the robustness and flexibility of the open source ecosystem of PostgreSQL, with the power and reliability of an enterprise-level cloud infrastructure such as Google Cloud Platform (GCP), offering a modern, scalable and ready to face critical workloads platform.
AlloyDB is positioned as an ideal solution for:
- Companies looking to modernize Oracle or SQL Server, environments, avoiding proprietary licenses.
- Critical workloads requiring high availability, low maintenance and dynamic scalability.
- Teams already working on Google Cloud and need to easily integrate artificial intelligence capabilities, advanced analytics and serverless services.
With AlloyDB, organizations can move towards a more agile, powerful and future-proof data infrastructure.
What is AlloyDB?
PostgreSQL is one of the most powerful and reliable open-source relational databases on the market. It uses the SQL language and is designed to handle complex workloads securely, efficiently, and scalably. Its development began in 1986, as part of the POSTGRES project at the University of California at Berkeley, and since then it has accumulated more than 35 years of continuous innovation.
Thanks to its robust architecture, focus on data integrity and committed global community, PostgreSQL has become the open source database of choice for businesses, governments and developers. It is highly extensible with advanced features such as PostGIS for geospatial data, compatible with multiple operating systems and compliant ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) principles since 2001, making it ideal for building modern, high-performance solutions.
On this solid foundation, Google Cloud developed AlloyDB, a fully managed relational database, fully compatible with PostgreSQL, including its most popular extensions. AlloyDB was designed specifically for enterprise environments that require extreme performance, high availability and uncompromised scalability.
In essence, AlloyDB is a cloud-optimized version of PostgreSQL that leverages key Google Cloud innovations in resiliency, reliability and operational efficiency. Existing applications and tools can continue to function without modification, thanks to its support for standard PostgreSQL connections and queries.
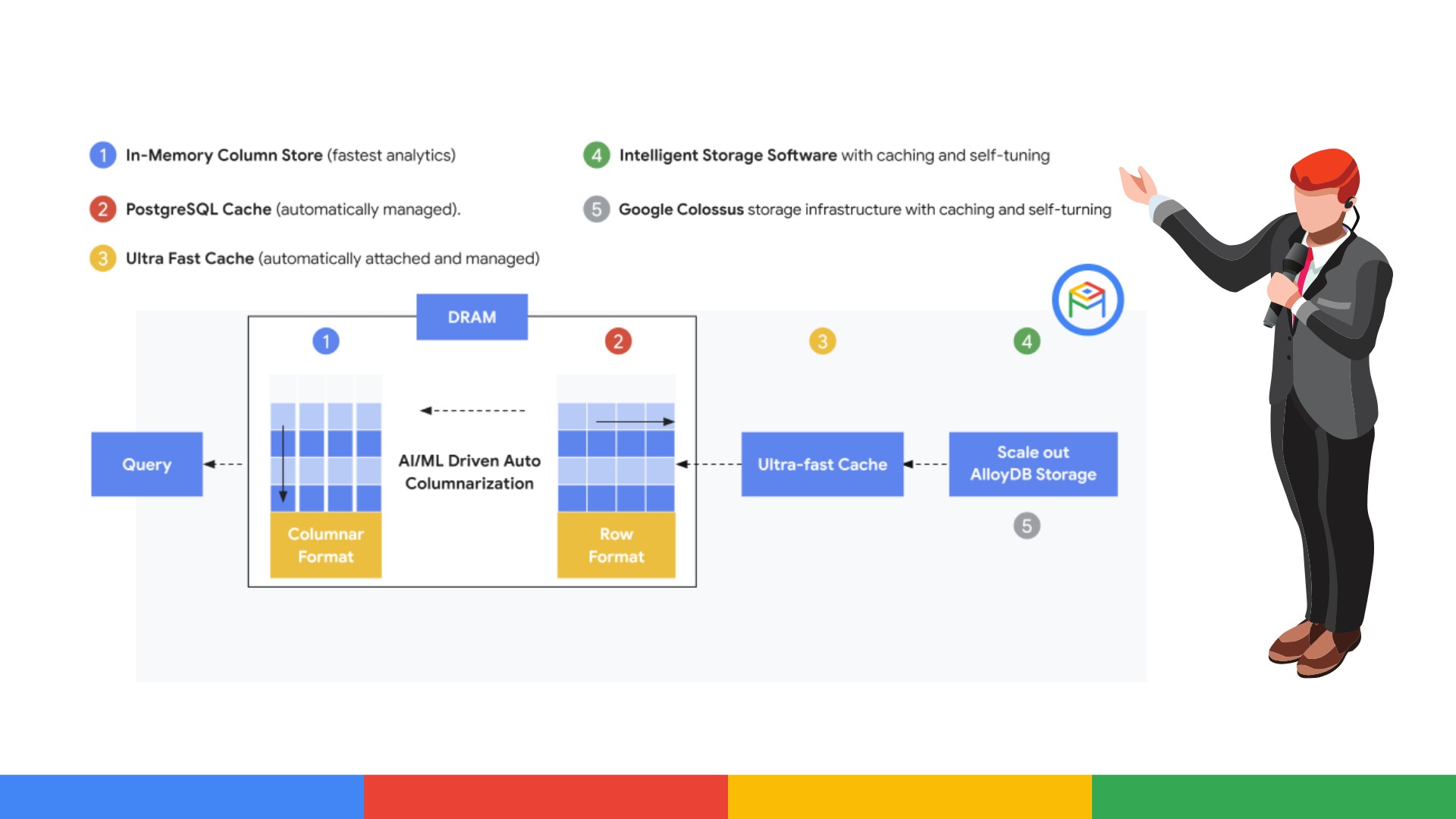
Its modern architecture separates compute from storage, allowing it to scale independently and efficiently. In addition, it integrates advanced technologies such as vectorized processing, persistent memory and predictive load analysis, maximizing response speed and reducing operational overhead.
History of AlloyDB for PostgreSQL
Google launched AlloyDB for PostgreSQL in May 2022 during the Google I/O event and later at Google Cloud Next, as a strategic response to the limitations of traditional cloud databases. Their goal was to offer a modern solution, natively designed for the cloud, seeking to optimize the performance and scalability of PostgreSQL, and also to demonstrate their expertise building world-class databases, based on proprietary technologies such as Spanner, Bigtable and Firestore.
Before the launch of AlloyDB, Google Cloud offered Cloud SQL, a managed service for databases such as PostgreSQL, MySQL and SQL Server. However, like other solutions on the market, it had limitations of traditional architectures, with poor optimization for mixed loads, storage bottlenecks and mostly vertical scalability. This left a gap for organizations that needed greater performance, flexibility and resiliency, especially in critical or data-intensive applications.
Common uses
- High performance transactional loads
Ideal for critical applications such as e-commerce, fintech or gaming. AlloyDB offers more than 4 times the performance of standard PostgreSQL thanks to its optimized architecture, allowing fast responses, flexible scalability and lower operational load.
Source: Google Cloud
- Real-time analytics
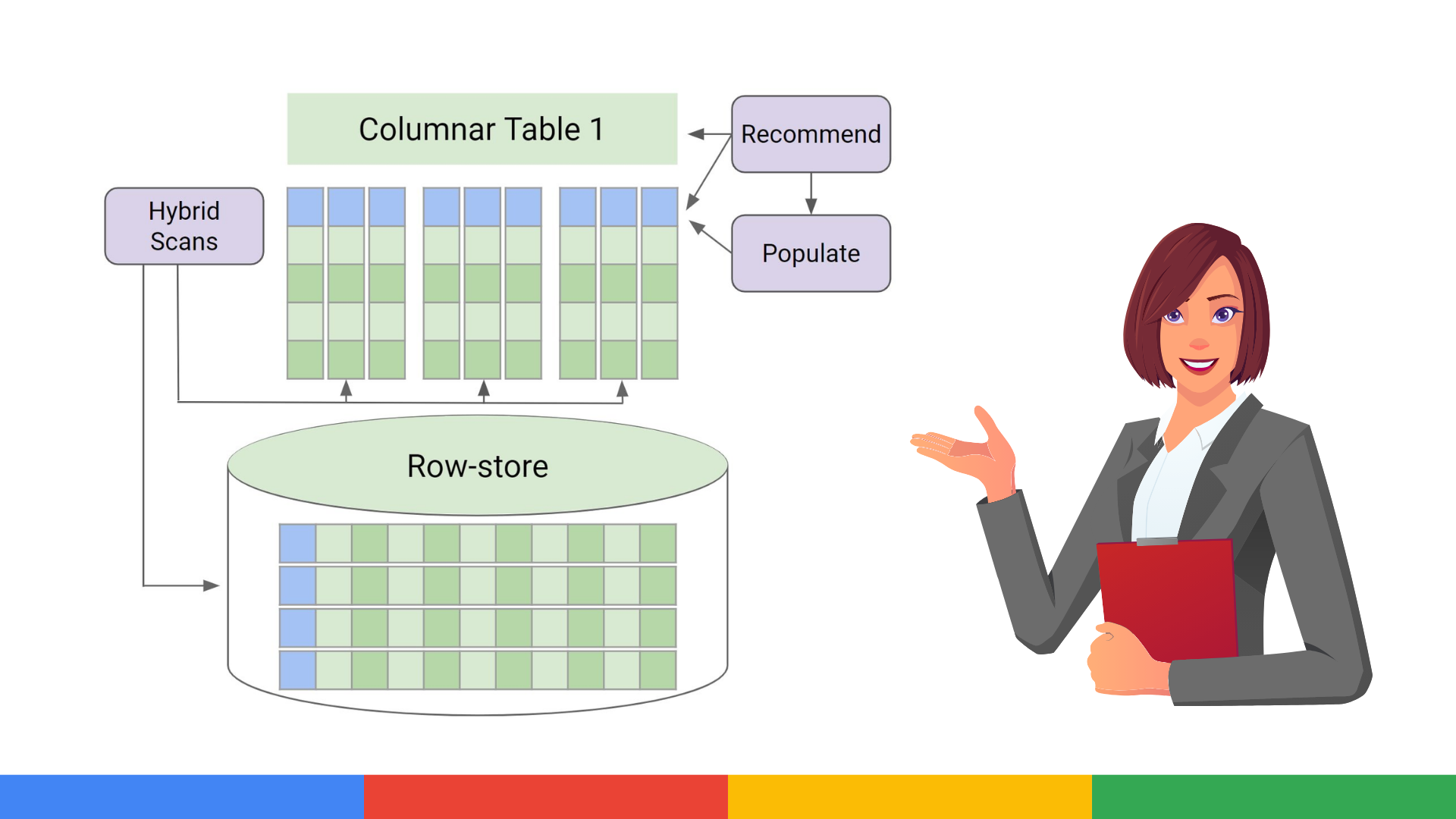
AlloyDB allows you to run analytical queries directly on operational data, with an integrated columnar engine that delivers up to 100 times faster than traditional PostgreSQL. Perfect for live dashboards, fraud detection and customer behavior analysis.
Source: Google Cloud
- Generative AI applications
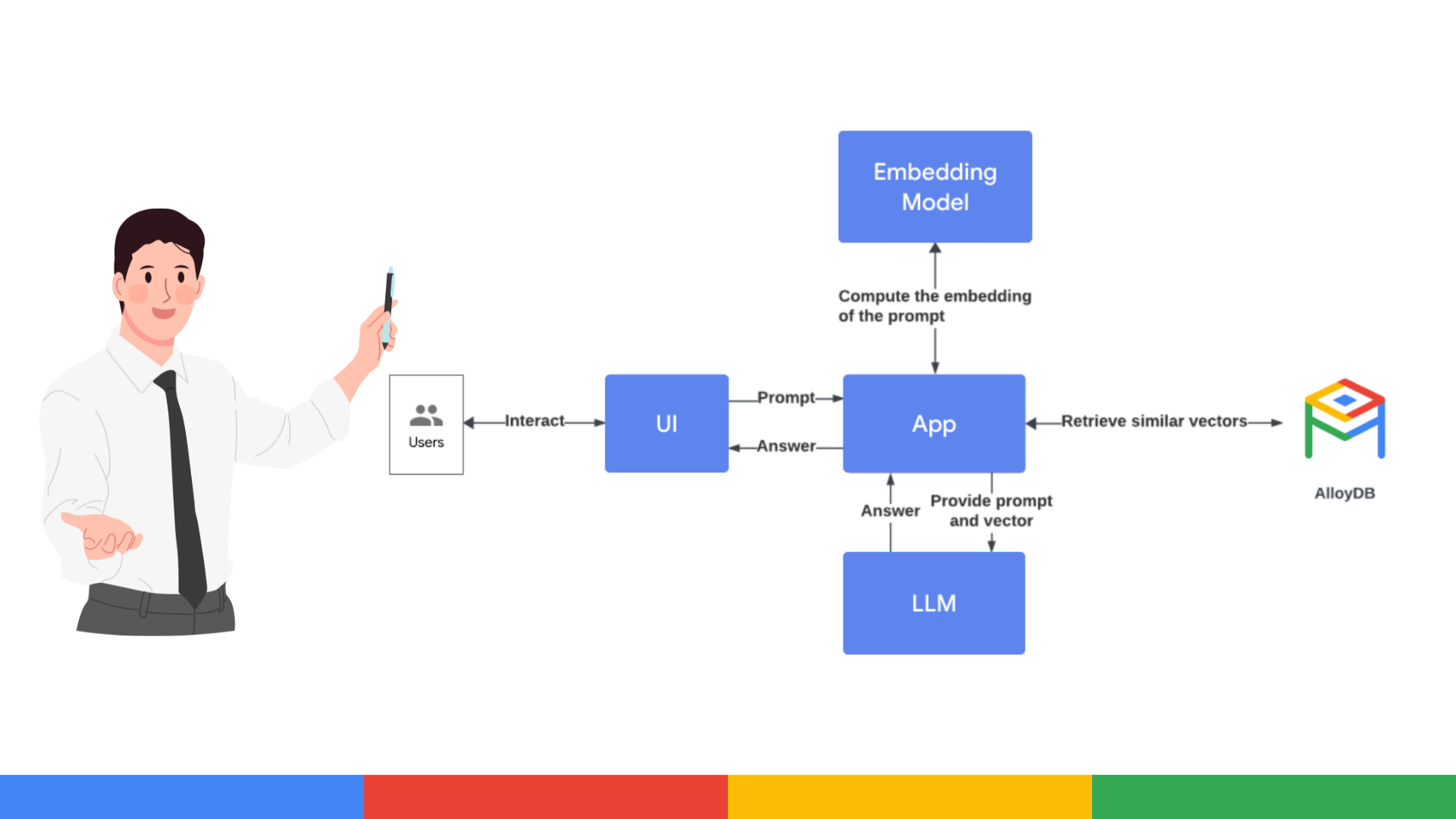
With AlloyDB AI, you can store and query vectors, generate embeddings directly from the database and connect with models in Vertex AI and other platforms, enabling assets such as chatbots, semantic search or advanced recommendation systems.
Source: Google Cloud
- Legacy database modernization
AlloyDB offers a simple path to migrate from PostgreSQL or other legacy databases such as Oracle or SQL Server, with support for tools such as Database Migration Service (DMS), obtaining a managed, scalable environment without proprietary licenses.
Source: Google Cloud
- Hybrid and multicloud deployments
AlloyDB Omni allows you to run the same AlloyDB engine in on-premises environments or in other clouds, making it easy to meet specific data sovereignty or regulatory requirements. It is a downloadable edition that offers the same functionality and performance as the cloud service, allowing you to standardize a single database across multiple environments with complete flexibility.
Source: Google Cloud
How does AlloyDB work?
Applications connect to AlloyDB in the same way they would connect to any standard PostgreSQL database, using the same protocols and query language. This means that no changes to existing applications are required to start using AlloyDB.
Behind the scenes, AlloyDB is built on a cloud-optimized architecture that combines different components designed to deliver high availability, maximum performance and high throughput. In addition, Google Cloud management tools allow you to monitor system health, and automatically adjust size and scale based on application demand, ensuring efficiency and operational continuity.
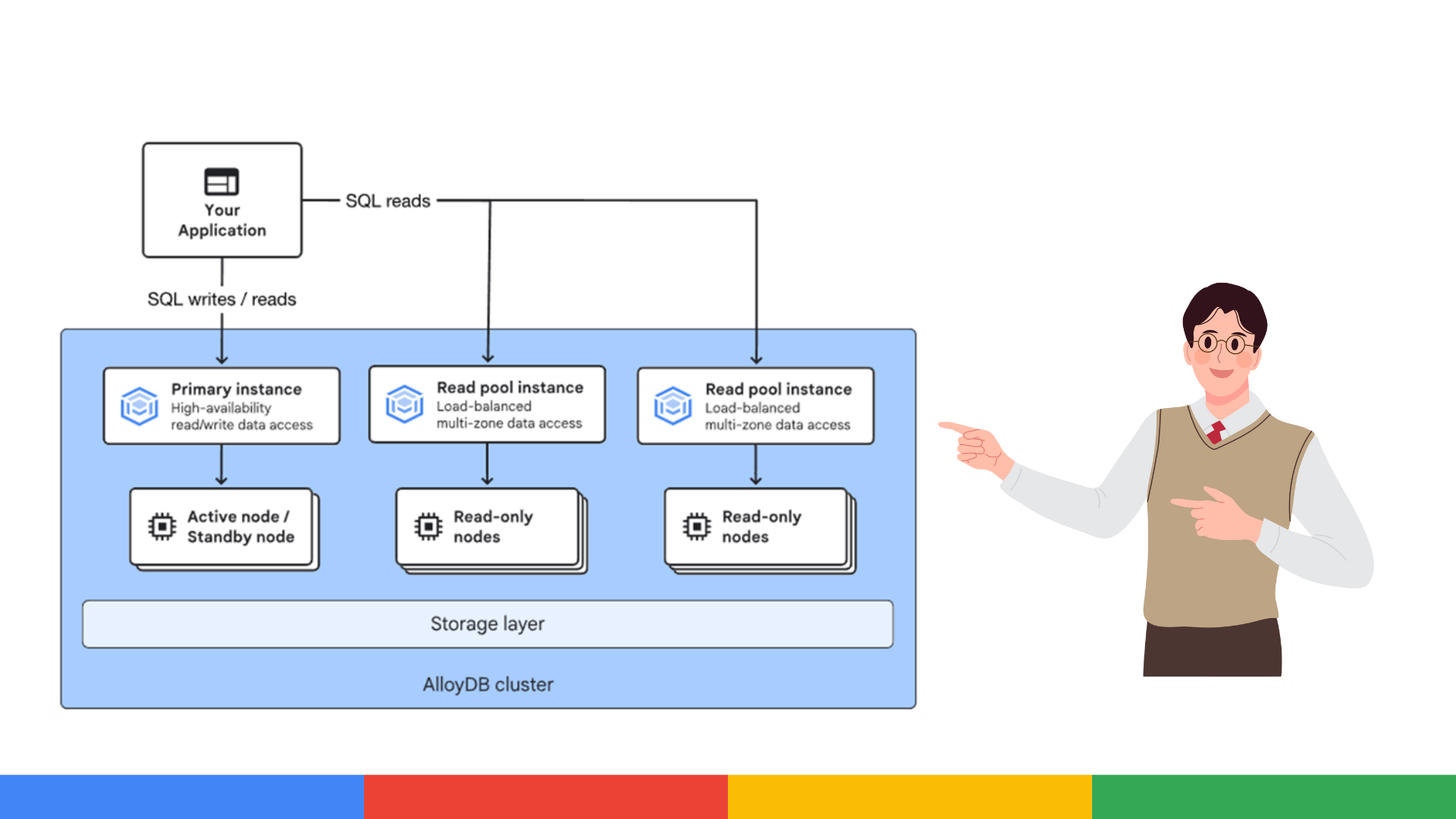
In AlloyDB, all the resources of a database deployment, logs and configurations are organized within a cluster, running in a single Google Cloud region and in a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
Each cluster consists of nodes, which are virtual machines running the PostgreSQL database engine. These nodes are grouped into instances, each with a private, static IP address in the VPC, allowing applications to easily connect using standard PostgreSQL protocols.
There are two types of instances in AlloyDB:
- Primary instance: It is the main access point for reading and writing. It can be configured as:
- High Availability (HA): It includes two nodes, one active and one standby, with automatic failover in the event of a failure.
- Basic: It has a single node and is designed for development or testing environments without critical availability requirements.
- Read pool instances: These are optional and are composed of one or more read-only nodes (up to 20 per cluster). AlloyDB automatically distributes queries among these nodes to improve performance.
In addition, AlloyDB allows instances to scale dynamically, adjusting the number of nodes, memory and compute capacity according to the needs of the application, without affecting the data or requiring long downtime. This is possible because data is stored separately in a flexible, compute-independent storage tier.
Source: Google Cloud
Conclusions
AlloyDB for PostgreSQL marks a significant advance in the evolution of relational databases in the cloud. It integrates the robustness and compatibility of the PostgreSQL open source ecosystem with a modern architecture, optimized from the ground up to deliver high performance, scalability and availability in demanding environments.
Unlike traditional solutions or legacy managed services, AlloyDB was built from the ground up as a truly cloud-native engine. It incorporates separation of compute and storage, persistent caching, continuous backup, and advanced capabilities for analytical, transactional, and generative AI workloads.
Resources
Review the following resources for learn more about the AllowDB:
Hope will be useful.
Follow us: